AI in QEHS – Part 1: AI for Safety Without Compromising Data Security

AI in QEHS – Part 1
AI for Safety: Intelligent Assistance Without Compromising Data Security
Artificial Intelligence is everywhere.
From generative chatbots to autonomous agents, AI promises productivity gains across nearly every business function. But in the world of Quality, Environmental, Health & Safety (QEHS), adoption must be approached differently.
Safety data is sensitive.
Incident investigations are confidential.
Regulatory exposure is real.
The question isn’t:
“Should we use AI?”
The real question is:
“How do we use AI responsibly — without compromising data security, privacy, or compliance?”
This article launches our multi-part series exploring how AI can enhance QEHS functions safely and strategically. We begin with the foundation: Safety Management.
Why Safety Is the Ideal Starting Point for AI
Safety programs generate high volumes of structured and unstructured data:
- Incident descriptions
- Near-miss reports
- Observations
- Corrective actions
- Risk assessments
- Root cause analyses
- Training records
Most organizations collect this data.
Few fully leverage it.
AI chatbots and intelligent agents can transform safety data from static records into dynamic, decision-support intelligence — if implemented correctly.
High-Impact AI Use Cases in Safety
1. Intelligent Incident Classification
When users submit an incident, AI can:
- Analyze free-text descriptions
- Suggest incident categories and subcategories
- Identify potential severity levels
- Flag regulatory reporting thresholds
This reduces:
- Misclassification errors
- Inconsistent data entry
- Reporting delays
It also improves long-term analytics accuracy and regulatory readiness.
2. Root Cause Assistance
AI agents can:
- Detect recurring patterns across sites
- Suggest potential contributing factors
- Recommend similar past corrective actions
- Highlight systemic risks
This does not replace human investigation.
It augments investigator capability with historical intelligence and cross-site visibility.
3. Proactive Risk Identification
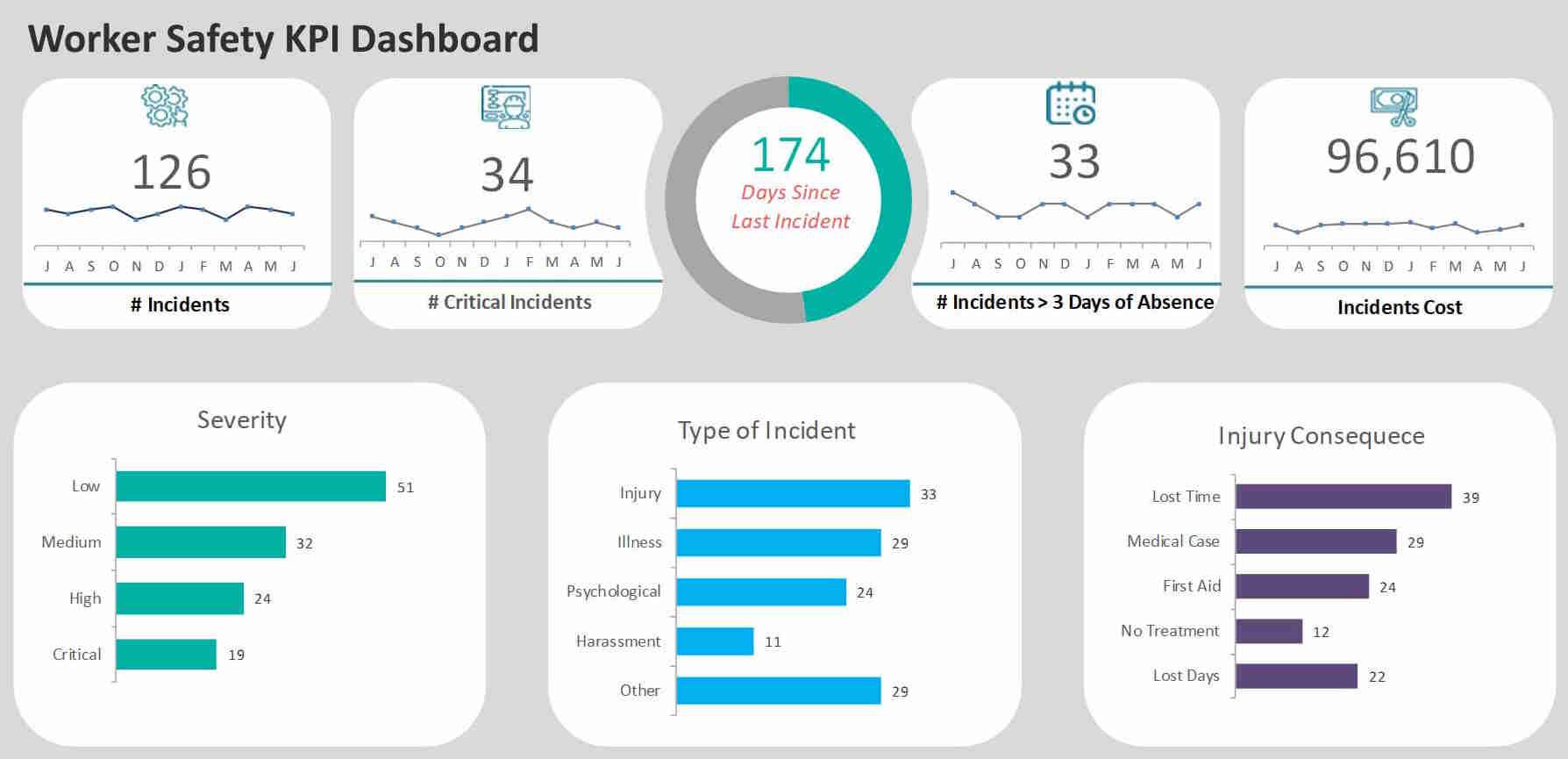
With sufficient historical data, AI models can:
- Identify leading indicators
- Detect rising trends before incidents occur
- Flag high-risk departments or tasks
- Surface anomalies in safety behavior reporting
Instead of reacting to incidents, organizations can intervene earlier.
4. AI Safety Assistants (Chatbots)
Modern safety chatbots can:
- Answer policy questions
- Guide users through reporting workflows
- Explain regulatory requirements
- Summarize incident trends for executives
- Provide instant KPI explanations
Imagine a plant manager asking:
“What were our top three injury drivers this quarter compared to last?”
And receiving an immediate, secure answer.
That’s the power of embedded AI — when deployed responsibly inside your controlled environment.
The Critical Issue: Data Security & Privacy
This is where many organizations hesitate — and rightly so.
Safety data often contains:
- Personal information
- Medical details
- Legal exposure
- Regulatory reporting obligations
- Sensitive operational data
Uploading that data into public AI tools is not acceptable.
Responsible AI adoption in QEHS must include:
Dedicated Hosting
AI models should operate within:
- Private cloud environments
- Customer-controlled infrastructure
- Isolated compute instances
No Public Data Sharing
- No training on client data
- No cross-customer learning
- No external model ingestion
Role-Based Access Controls
AI responses must respect:
- Site-level access
- Departmental permissions
- Legal privilege boundaries
Auditability
Every AI-generated recommendation should be:
- Logged
- Traceable
- Reviewable
AI must be accountable.
AI Chatbots vs. AI Agents in Safety
Understanding the difference matters.
AI Chatbot
- Responds to user prompts
- Provides guidance and insights
- Assists with reporting and analytics
AI Agent
- Performs tasks autonomously
- Monitors risk trends continuously
- Escalates anomalies
- Triggers workflows
In safety management, most organizations begin with chatbot augmentation — and gradually evolve toward supervised agents.
Autonomy should be earned, not assumed.
Governance: The Overlooked Pillar
Technology alone is not enough.
Organizations adopting AI in safety should define:
- AI usage policies
- Validation processes
- Human oversight checkpoints
- Model update controls
- Security review protocols
AI must operate inside your governance framework — not outside it.
A Phased Approach to AI in Safety
Phase 1 – Augmented Intelligence
- Incident classification assistance
- Safety chatbot for knowledge access
Phase 2 – Analytical Enhancement
- Pattern detection
- Trend forecasting
- KPI narrative summaries
Phase 3 – Supervised Agents
- Automated risk monitoring
- Escalation triggers
- Predictive intervention alerts
Each phase builds confidence, control, and measurable ROI.
The Strategic Advantage
When implemented securely, AI in safety delivers:
- Faster reporting cycles
- Improved data quality
- Reduced administrative burden
- Better executive visibility
- Earlier risk detection
- More consistent global operations
Most importantly, it allows safety professionals to focus on prevention — not paperwork.
What’s Next in This Series
In upcoming articles, we will explore AI applications across:
- Environmental compliance
- Industrial hygiene
- Audit & inspections
- Safe Work Permits
- Responsible Care & ESG reporting
Each through the same lens:
Innovation without compromising security.
Final Thought
AI in QEHS is not about replacing professionals.
It is about equipping them with intelligent tools that operate inside secure, governed environments.
The future of safety isn’t just digital.
It’s intelligent — responsibly.
Ready to revolutionize your safety management? Discover how our QEHS SaaS platform can help your organization lead in the digital age of occupational health and safety.
Request a Demo or Contact Us to learn more.
